What is Geofabric Bidim and its Applications in Civil Engineering?
Geofabric Bidim has gained significant traction in civil engineering due to its versatile applications. Recent studies indicate that over 50% of civil projects now rely on geotextiles for improved durability and performance. “Geofabric Bidim transforms how we approach soil stabilization,” says Dr. Alan Smith, a leading expert in geotechnical engineering. His insights highlight the material’s pivotal role in enhancing infrastructure resilience.
With increasing urbanization and climate challenges, the construction industry faces pressing demands. Geofabric Bidim not only aids in water drainage but also minimizes erosion. This product is crucial for road construction, providing solid foundations while reducing maintenance costs. Its effectiveness in managing sediment flow has been demonstrated in several large-scale projects.
However, there is a need for more rigorous testing to assess long-term performance in various conditions. While Geofabric Bidim offers numerous advantages, potential limitations must also be addressed. Industry professionals must continue exploring and refining its applications to ensure sustainable development. This ongoing discourse is vital for achieving optimal results in future civil engineering projects.
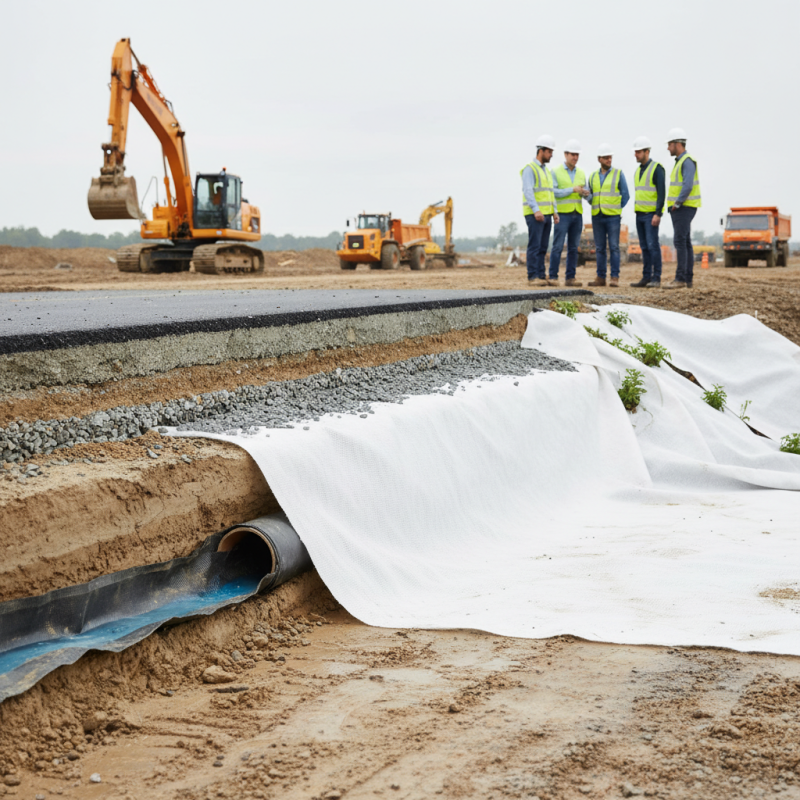

What is Geofabric Bidim? An Overview of Its Composition and Features
Geofabric Bidim is a geotextile widely used in civil engineering projects. It comprises non-woven fabric made from synthetic fibers. The material is known for its durability and strength. Bidim effectively separates layers in construction sites, optimizing soil performance. According to industry reports, the global geotextiles market is expected to reach $10 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing demand for materials like Bidim.
One notable feature of Bidim is its permeability. This allows water to flow freely while retaining soil particles. However, this characteristic can lead to challenges. If not properly installed, Bidim can fail to provide the needed support, causing structural issues. It’s crucial for engineers to assess site conditions carefully. Proper design and installation mitigate potential risks associated with this material.
In applications like road construction, Bidim enhances stability. It prevents erosion and prolongs the lifespan of infrastructure. Yet, improper usage can lead to compromised performance. Real-world data notes that up to 30% of geotextile installations encounter issues due to inadequate planning. Therefore, while Bidim offers significant benefits, a thoughtful approach is critical to its successful application.
The Importance of Geofabric Bidim in Soil Stabilization Techniques
Geofabric Bidim plays a pivotal role in soil stabilization techniques. Its use helps manage water flow and prevent soil erosion. This geofabric is often installed in construction sites, roadway projects, and landscaping designs. The material's structure is designed to support different soil types effectively. By reinforcing the soil, it enhances the stability of structures built on top.
In many cases, soil destabilization occurs due to poor drainage or heavy rainfall. Geofabric Bidim offers a solution by allowing water to filter through while maintaining soil integrity. However, the application requires careful consideration. A misjudgment in the type of geofabric or its installation can lead to ineffective stabilization.
Furthermore, while Geofabric Bidim can improve soil behavior, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each project has unique conditions that must be assessed. Environmental factors, soil composition, and drainage patterns all influence the effectiveness of this technique. Engineers must remain vigilant and continuously learn from past implementations.
Applications of Geofabric Bidim in Drainage Systems and Erosion Control
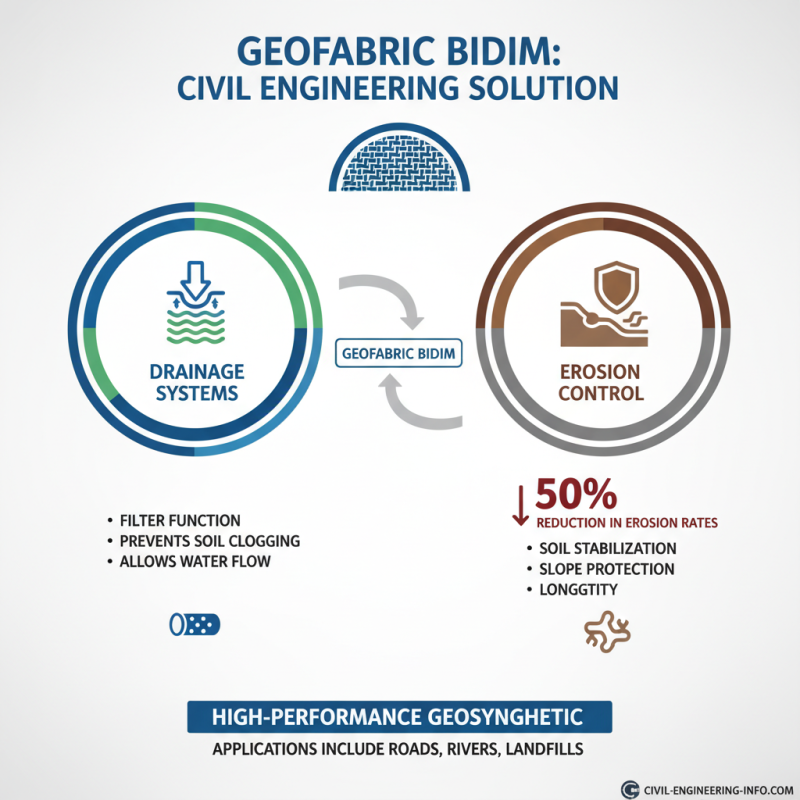
Geofabric Bidim is a high-performance material widely used in civil engineering. Its applications extend significantly into drainage systems and erosion control. This geosynthetic fabric serves as a filter, preventing soil erosion while allowing water flow. Reports indicate that using geofabric can reduce erosion rates by up to 50% in specific conditions.
In drainage systems, Geofabric Bidim enhances efficiency. It allows for optimal water management in construction sites and landscapes. When used properly, it can maintain soil integrity, extending the life of drainage systems. A study by the Geosynthetics Institute found that proper implementation of geofabrics can lead to a 30% increase in drainage effectiveness.
Tips: Always ensure proper installation techniques. Misalignment may lead to reduced efficiency. Remember that environmental factors can also impact performance. Regular site assessments can help in monitoring the effectiveness of the geofabric. Keeping in mind these practices is crucial for achieving desired results.
Cost-Effectiveness of Geofabric Bidim in Civil Engineering Projects
Geofabric Bidim has gained attention in civil engineering for its cost-effectiveness. This versatile material serves multiple purposes in various projects. It is essential for soil stabilization, drainage, and erosion control. According to a 2022 industry report, using geofabric can reduce overall project costs by up to 30%. This reduction can be crucial for budget-restricted projects.
In addition to cost savings, Bidim’s efficiency lies in its ability to enhance the lifespan of a project. A study by the Global Geosynthetics Alliance indicated that incorporating geofabric can extend the life of infrastructure by nearly 25%. By reinforcing soil and controlling water flow, it minimizes erosion risks and increases stability. However, it is vital to consider site-specific conditions. Not all terrains will see the same benefits, and over-reliance on geofabric may lead to unforeseen complications.
Despite its advantages, some setbacks exist. The installation process can be challenging, requiring skilled labor to ensure optimal performance. If improperly installed, the intended benefits may not be realized. Therefore, ongoing assessments and adjustments in application techniques remain essential. Focusing on training and development can help mitigate these risks, ensuring that civil engineers reap the maximum rewards of Geofabric Bidim.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations of Geofabric Bidim Worldwide
Geofabric Bidim is gaining traction in civil engineering. It serves various purposes, particularly in sediment control and erosion reduction. One notable case study comes from a coastal town facing severe beach erosion. Engineers utilized Geofabric Bidim to create barriers that helped stabilize the shoreline. This application not only protected local infrastructure but also restored habitats.
Another example is found in a major urban development project. The city faced challenges with stormwater management. Implementing Geofabric Bidim in drainage systems allowed for better water filtration. However, this method had mixed results. While it improved drainage, some areas still experienced flooding. Local authorities learned there’s no one-size-fits-all approach. Each project requires a tailored strategy, considering soil conditions and environmental factors.
Related Posts
-

Exploring the Benefits of Woven Geofabric in Sustainable Construction Practices
-

Exploring the Environmental Benefits of Geotextile Mats in Modern Construction
-

Top 10 Uses of Geotech Fabric in Modern Civil Engineering
-

What is Geotextile Tape and How is it Used in Construction?
-

Exploring Innovations in Gsm Geotextile at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Top 5 Benefits of Using Cement Blankets for Construction Projects
-

Phone
-

E-mail
-

Whatsapp
-

Top